| Month | CPR | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 50% PSA | 100% PSA | 200% PSA | |
| 1 | 0.1% | 0.2% | 0.4% |
| 2 | 0.2% | 0.4% | 0.8% |
| 3 | 0.3% | 0.6% | 1.2% |
| 29 | 2.9% | 5.8% | 11.6% |
| 30 | 3.0% | 6.0% | 12.0% |
| 31 | 3.0% | 6.0% | 12.0% |
| 32 | 3.0% | 6.0% | 12.0% |
eMBS uses the two most common prepayment models: CPR (Conditional Prepayment Rate, also known as Constant Prepayment Rate) and PSA (originally named for the Public Securities Association, now known as the Bond Market Association, who now call PSA "Prepayment Speed Assumption").
The CPR is computed by comparing the actual factor for the current month with the factor that would be expected given normal amortization from the previous month's factor. The difference between the expected and the actual factors represents the amount of unscheduled prepayments of principal from the underlying mortgage loans.
The percentage difference between the expected factor and the actual factor is called the Single Monthly Mortality, or SMM. CPR is calculated by annualizing the SMM; the resulting CPR can be thought of as the fraction that would prepay if the SMM rate remained steady for 12 months.
Most factors are effective on the first of the current month, June 1 for example, and are reported during the first few days of the month. The prepayments reflected in the 6/1 factor were gathered by the loan servicer during May. The 6/1 factor is used to calculate May's prepayment rate; June's prepayment rate will not be known until the 7/1 factors are released.
To convert between CPR and SMM:
(1 - CPR/100) = (1 - SMM/100)12
and
(1 - SMM/100) = (1 - CPR/100)1/12
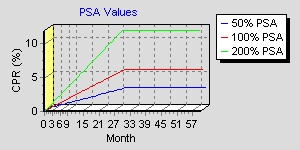
The PSA measure compares the actual
CPR to the expected or standard CPR as defined by the Public Securities
Association. The PSA model assumes that prepayments increase monthly
until the 30th month, when they become constant.

| Month | CPR | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 50% PSA | 100% PSA | 200% PSA | |
| 1 | 0.1% | 0.2% | 0.4% |
| 2 | 0.2% | 0.4% | 0.8% |
| 3 | 0.3% | 0.6% | 1.2% |
| 29 | 2.9% | 5.8% | 11.6% |
| 30 | 3.0% | 6.0% | 12.0% |
| 31 | 3.0% | 6.0% | 12.0% |
| 32 | 3.0% | 6.0% | 12.0% |
The general calculation method for CPR between any 2 dates (from Mark Gordon and Michael Waldman's "Determining the Yield of a Mortgage Security") uses these variables:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| U | Starting Factor |
| V | Ending Factor |
| m | Starting WAM |
| k | Number Months in Time Period |
| c | Monthly Coupon = WAC/12 |
To compute W (the factor at the end of the time period if there had been no prepayments):
| W = U * | (1+c)m - (1+c)k |
| (1+c)m - 1 |
Then it's possible to compute the CPR:
| CPR = 100*( 1 - ( | V | )12/k ) |
| W |
The PSA is valid only for securities that amortize over 30 years. This includes balloons that have a term of less than 30 years, but use 30 year amortization.
The PSA value is calculated using the prepay month number and CPR. for a pool's 1-month PSA, the prepay month number is the weighted-average loan age, or WALA; for a pool's multi-month PSA, it's WALA + 1, which is the WALA at the end of the month.
The formula is:
For a multi-month PSA average, e.g. a 3, 6, or 12-month average PSA, if the prepay month number < 30, the
model is non-linear, so we must iterate to get the PSA.
The eMBS code used to compute Prepayments and other Analytics is available for use in your internal systems. For more information, email embs_support@bkfs.com .
Copyright ©1999 eMBS Inc. All rights reserved.